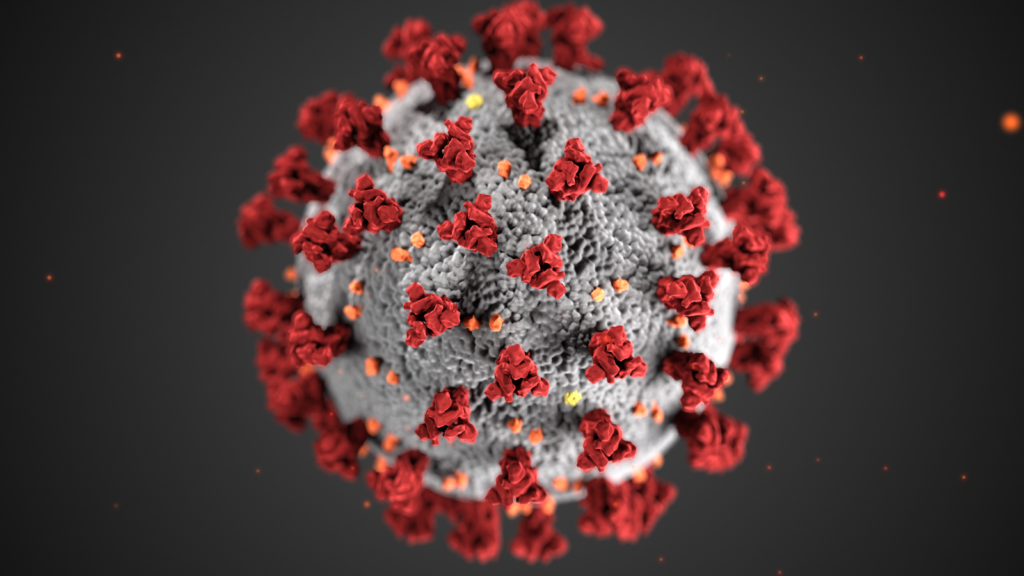
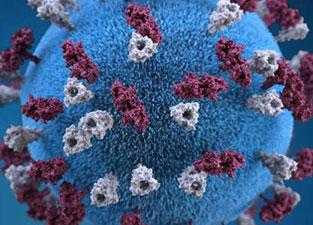
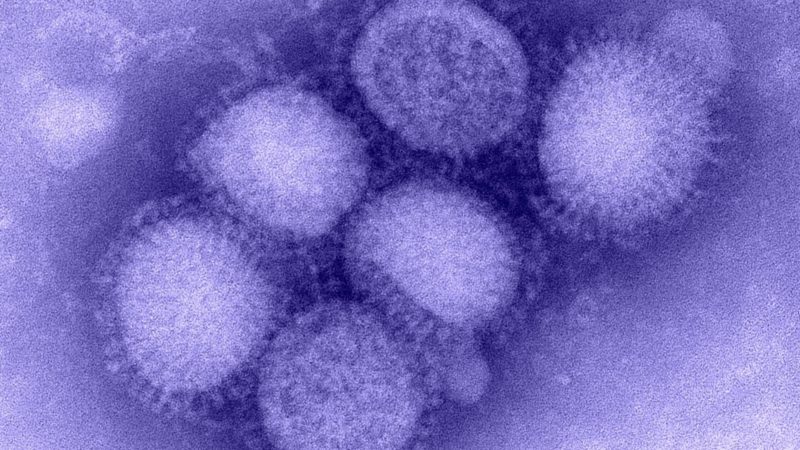
Viruses are microscopic parasites which inject their genetic information into host cells. The genetic information can be either RNA or DNA. Viruses are different from other parasites in this guide because they are not truly alive and do not have a place on the phylogenetic tree. They do not intake food, grow, or store energy on their own. Viruses can infect any form of life.
Many human viruses, including the ones below, are zoonotic. This means that they began as viruses specialized to a reservoir host and then jumped to human hosts. Zoonotic viruses are more likely when the virus genetic information is RNA, because this has the ability to mutate more easily. Below I give examples of six viruses which have had a large impact on humans: coronavirus, measles, Zika, Avian flu, HIV, and Ebola virus.
https://www.the-scientist.com/feature/characteristics-that-give-viruses-pandemic-potential-67822
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uIut0oVWCEg
https://www.cdc.gov/measles/about/history.html
https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/zika-virus-disease
https://www.ioes.ucla.edu/project/avian-influenza-virus-north-american-migratory-birds/
https://www.nfid.org/infectious-diseases/hiv-aids/
https://abcnews.go.com/Health/ebola-/story?id=24733669
SimBio 2021